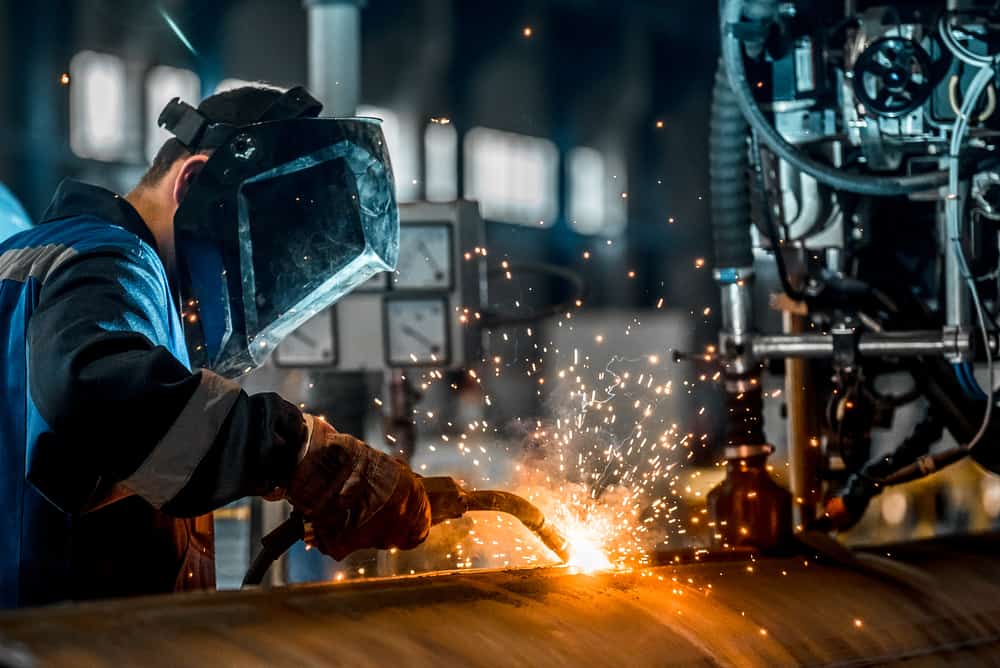
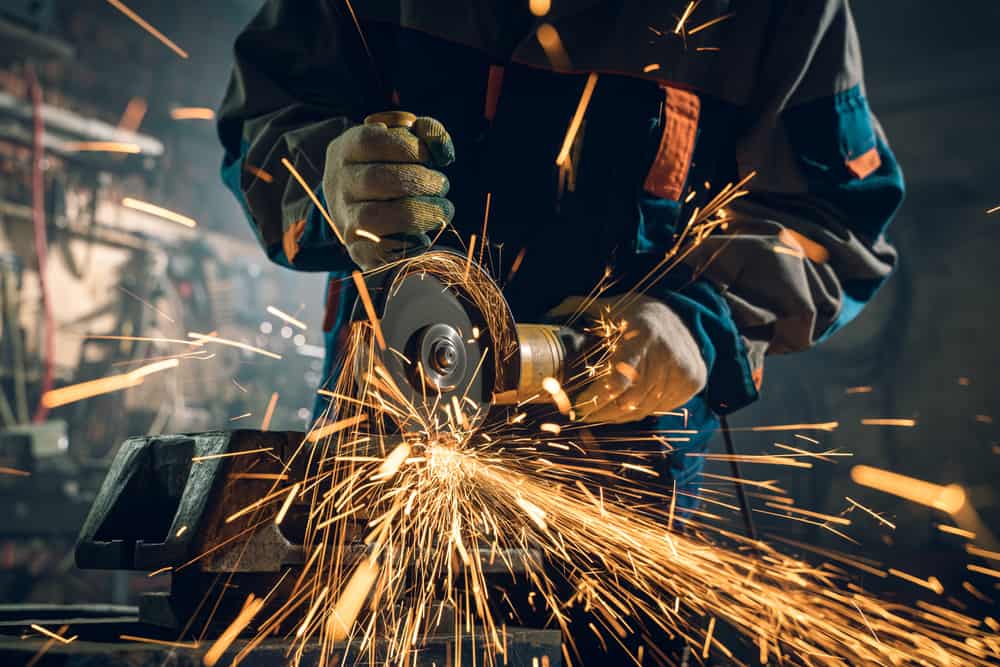
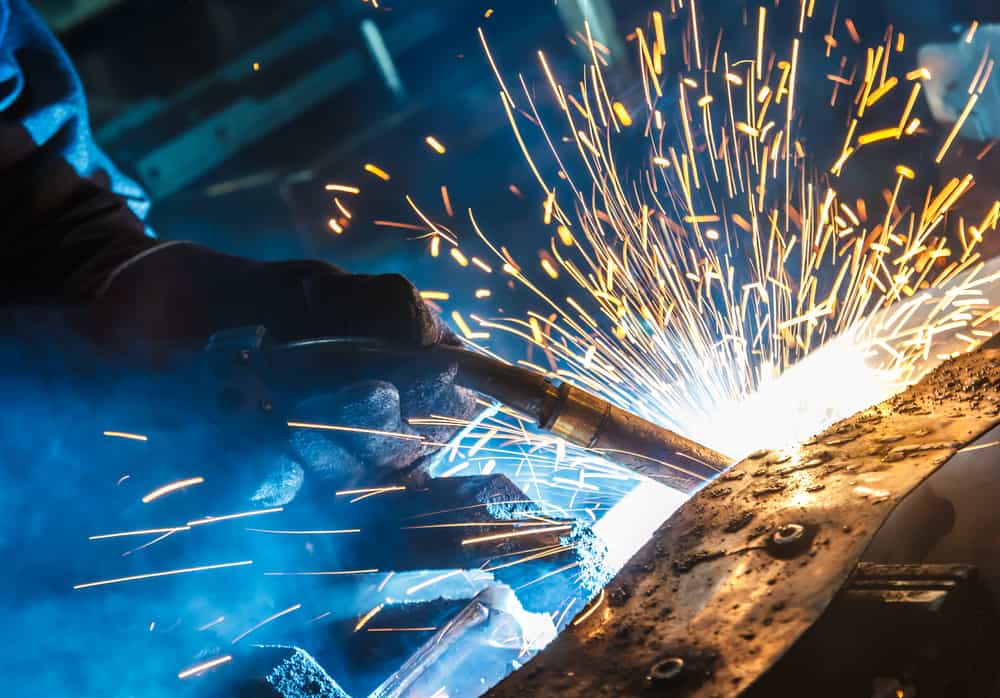
Fabrication is a fundamental process used across various industries to transform raw materials or semi-finished products into finished goods, components, or structures. It involves a series of manufacturing activities such as cutting, shaping, bending, welding, machining, and assembling to create products with specific designs, dimensions, and functionalities.
Fabrication is integral to industries ranging from construction and manufacturing to transportation and energy production, providing essential components, equipment, and infrastructure to support modern society’s needs. It encompasses the conversion of raw materials such as metal, plastic, wood, and composite materials into usable forms through a combination of mechanical, thermal, and chemical processes.
This process often begins with the interpretation of engineering drawings, specifications, or digital models that outline the desired product’s dimensions, materials, and tolerances. Skilled fabricators then employ a variety of techniques and tools to manipulate the materials into the required shapes and sizes, adhering to precise standards and quality control measures throughout the production process.
Fabrication techniques vary depending on the specific requirements of the industry and the nature of the end product. For instance, in metal fabrication, common methods include cutting with saws, lasers, or plasma torches, followed by shaping using presses, brakes, or rolling mills. Welding, soldering, or brazing may be employed to join metal components together, while finishing processes such as grinding, polishing, or painting are applied to enhance aesthetics and durability.
Similarly, in industries like plastics or wood fabrication, specialised tools and processes are used to mould, shape, or laminate materials into the desired forms, often with a focus on precision and repeatability. fabrication plays a critical role in manufacturing, construction, infrastructure development, and numerous other sectors, enabling the creation of a wide range of products and structures that form the backbone of modern society. From intricate machine parts to massive steel structures and complex electronic assemblies, the art and science of fabrication are essential for driving innovation, efficiency, and progress across diverse industries and applications.
The Varied Benefits Of Fabrication Across The Industries
Fabrication offers numerous benefits across various industries, contributing to efficiency, flexibility, customisation, and cost-effectiveness. Here are some key advantages of fabrication:
Customisation: Fabrication allows for the creation of highly customised products tailored to specific requirements, dimensions, and functionalities. This flexibility enables manufacturers to meet the unique needs of customers and address diverse market demands effectively.
Versatility: Fabrication techniques can be applied to a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, wood, composites, and more. This versatility allows for the production of a diverse array of products, components, and structures across different industries and applications.
Efficiency: By employing advanced machinery, automation, and precision tools, fabrication processes can achieve high levels of efficiency and productivity. This results in faster production times, reduced lead times, and improved throughput, enabling manufacturers to meet deadlines and optimise their operations.
Quality Control: Fabrication workflows often incorporate stringent quality control measures to ensure the consistency, accuracy, and integrity of finished products. By implementing quality assurance protocols and inspection procedures, manufacturers can uphold high standards of product quality and reliability.
Cost-Effectiveness: While initial setup costs for fabrication may be significant, mass production and economies of scale often lead to lower unit costs over time. Additionally, fabrication allows for efficient use of materials, minimization of waste, and optimization of production processes, all of which contribute to cost savings in the long run.
Innovation: Fabrication encourages innovation and creativity by providing designers and engineers with the freedom to explore new materials, designs, and manufacturing techniques. This fosters continuous improvement, product innovation, and technological advancements across various industries.
Adaptability: Fabrication processes can adapt to changing market trends, customer preferences, and technological advancements with relative ease. Manufacturers can quickly reconfigure production setups, introduce new product lines, or modify existing designs to respond to evolving market demands and competitive pressures.
Sustainability: Fabrication technologies and practices can be optimised to minimise environmental impact and promote sustainability. Strategies such as recycling, waste reduction, energy efficiency, and the use of eco-friendly materials contribute to sustainable manufacturing practices that benefit both businesses and the environment.
Overall, fabrication offers a multitude of benefits that empower manufacturers to create high-quality, customised products efficiently, adapt to market dynamics effectively, and drive innovation and sustainability in the manufacturing sector.
Fabrication Across The Industries
There are different types of fabrication needs and techniques across varied industries. We discuss the main ones below.
Mining:
- Fabrication involves the construction of various equipment used in mining operations, such as:
- Crushers: Machines used to break down large rocks into smaller pieces for easier handling and processing.
- Conveyor systems: Systems used to transport mined materials from one location to another within the mine or to processing facilities.
- Processing plants: Facilities where mined materials are processed and refined to extract desired minerals.
Steel:
- Fabrication in the steel industry encompasses a wide range of processes and products, including:
- Structural steel: Beams, columns, and other structural components used in building construction.
- Pipes and tubes: Used in various applications such as infrastructure, oil and gas pipelines, and automotive exhaust systems.
- Sheet metal fabrication: Cutting, bending, and welding of sheet metal to create components for machinery, appliances, and automotive bodies.
Cement:
- Fabrication in the cement industry involves the construction of cement plants and the manufacturing of equipment such as:
- Kilns: Large rotating furnaces where raw materials are heated to high temperatures to produce clinker, the primary ingredient in cement.
- Cement mills: Equipment used to grind clinker and other additives into a fine powder, which is then mixed with gypsum to produce cement.
- Silos and storage tanks: Structures used to store raw materials, intermediate products, and finished cement.
Coal:
- Fabrication in the coal industry includes the production of equipment used in coal mining, processing, transportation, and power generation, such as:
- Conveyor systems: Used to transport coal from mines to processing plants or storage facilities.
- Coal crushers: Machines used to reduce the size of coal particles for easier handling and processing.
- Power plant components: Boilers, turbines, and generators used in coal-fired power plants to generate electricity.
Rail:
- Fabrication in the rail industry involves the manufacturing of various components for railway infrastructure and rolling stock, including:
- Railway tracks: Rails, sleepers, and fastening systems used to construct railway lines.
- Locomotives: Diesel or electric-powered engines used to pull trains.
- Rolling stock: Wagons, passenger cars, and freight cars used to transport goods and passengers.
Quarries:
- Fabrication in quarries includes the production of equipment used in extracting and processing aggregates, stones, and minerals, such as:
- Crushers and screens: Machinery used to crush and screen raw materials extracted from quarries.
- Loaders and excavators: Equipment used to load mined materials onto trucks for transportation.
- Conveyor systems: Used to transport materials from the quarry to processing plants or storage facilities.
Power Generation:
- Fabrication in power generation involves the manufacturing of equipment and components for various types of power plants, including:
- Turbines: Steam turbines, gas turbines, and hydro turbines used to convert the energy from fuel or water into mechanical energy.
- Generators: Machines that convert mechanical energy into electricity.
- Boilers: Pressure vessels used to produce steam for driving turbines in coal-fired, gas-fired, or nuclear power plants.
Renewable Energy:
- Fabrication in renewable energy includes the production of components for solar, wind, hydroelectric, and biomass facilities, such as:
- Solar panels: Photovoltaic cells, frames, and mounting systems used to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity.
- Wind turbine components: Blades, towers, and nacelles used to harness wind energy and generate electricity.
- Hydroelectric equipment: Turbines, generators, and dams used to capture the energy of flowing water and convert it into electricity.
Waterways:
- Fabrication in waterways involves the manufacturing of vessels, infrastructure, and equipment used in marine transportation and recreation, including:
- Ships and boats: Vessels of various sizes and types used for transporting goods and passengers, fishing, or recreational activities.
- Docks and piers: Structures built along shorelines or in harbours for mooring vessels and loading/unloading cargo.
- Marine equipment: Cranes, winches, and navigation aids used in ports, harbours, and inland waterways.
Food Processing and Production:
- Fabrication in the food industry includes the construction of processing equipment and machinery used in the manufacturing and packaging of food and beverages, such as:
- Mixing and blending equipment: Machines used to mix ingredients and create food products such as sauces, dough, and batter.
- Heat processing equipment: Ovens, cookers, and pasteurizers used to cook, bake, or sterilise food products.
- Packaging machinery: Filling, sealing, and labelling machines used to package food products in containers such as bottles, cans, and pouches.
Fabrication is a major development in modern manufacturing, offering a number of advantages across diverse industries and applications. From its ability to deliver highly customised products to its versatility in working with various materials, it drives efficiency, flexibility, and innovation in production processes. The benefits of fabrication extend beyond cost-effectiveness and quality control to encompass adaptability, sustainability, and the fostering of continuous improvement and technological advancement.
As manufacturers strive to meet the evolving needs of customers, respond to market dynamics, and address sustainability challenges, fabrication is key. By harnessing advanced technologies, embracing best practices, and prioritising innovation, businesses can leverage fabrication for growth, competitiveness, and success in today’s dynamic manufacturing landscape.
Are you in need of fabrication services tailored to your specific industry needs? Look no further than Jones Complete Services. With our state-of-the-art fabrication workshop located in the Illawarra region, we are perfectly positioned to meet your requirements for spare parts and components across a wide range of industries, including Mining, Steel, Cement, Coal, Rail, Quarries, Power Generation, Renewable Energy, Waterways, Food Processing, and Production.
At Jones Complete Services, we pride ourselves on delivering exceptional quality and precision in every project we undertake. Whether you require workshop fabrication or onsite services, our experienced team is equipped to handle all your fabrication needs from start to finish. From site and workshop plasma cutting to sheet metal fabrication, machining, assembly, and quality control, we have the expertise and capabilities to ensure your project is completed to the highest standards.
Choose Jones Complete Services as your trusted partner for all your fabrication needs, and experience the difference our expertise and dedication can make. Contact us today to discuss how we can assist you with your fabrication tasks and take your project to the next level!